线性回归模型
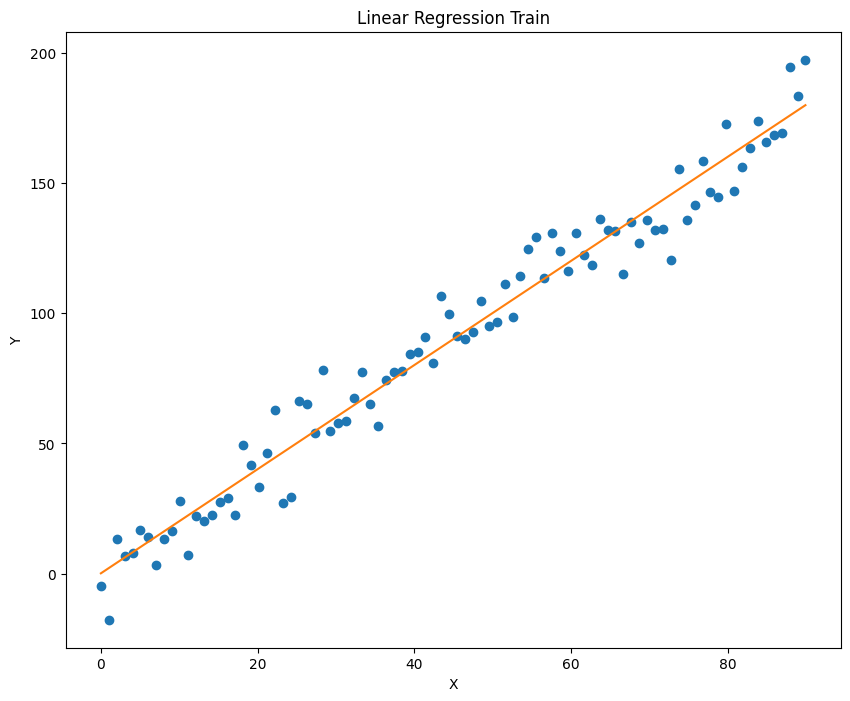
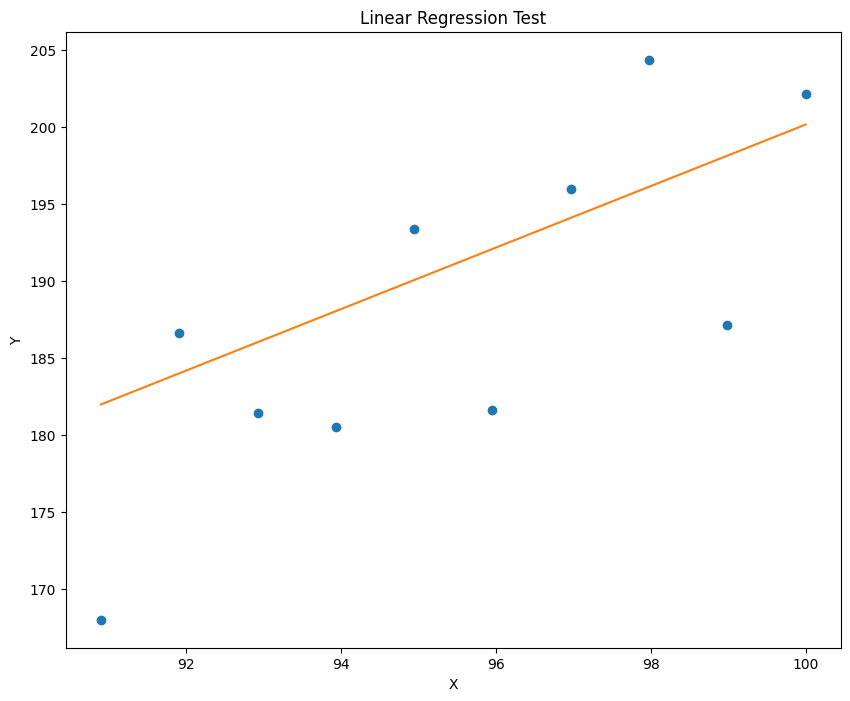
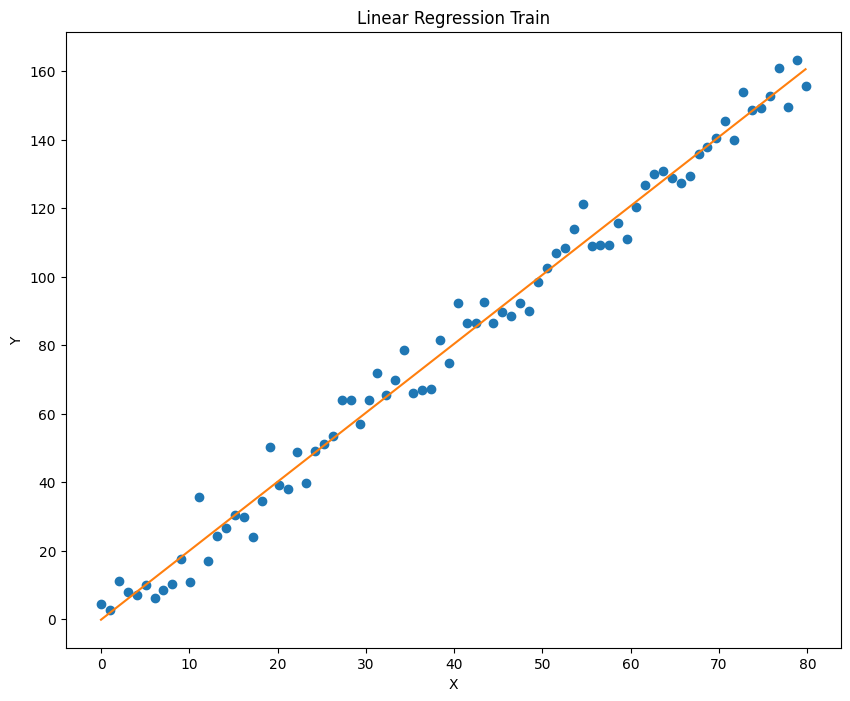
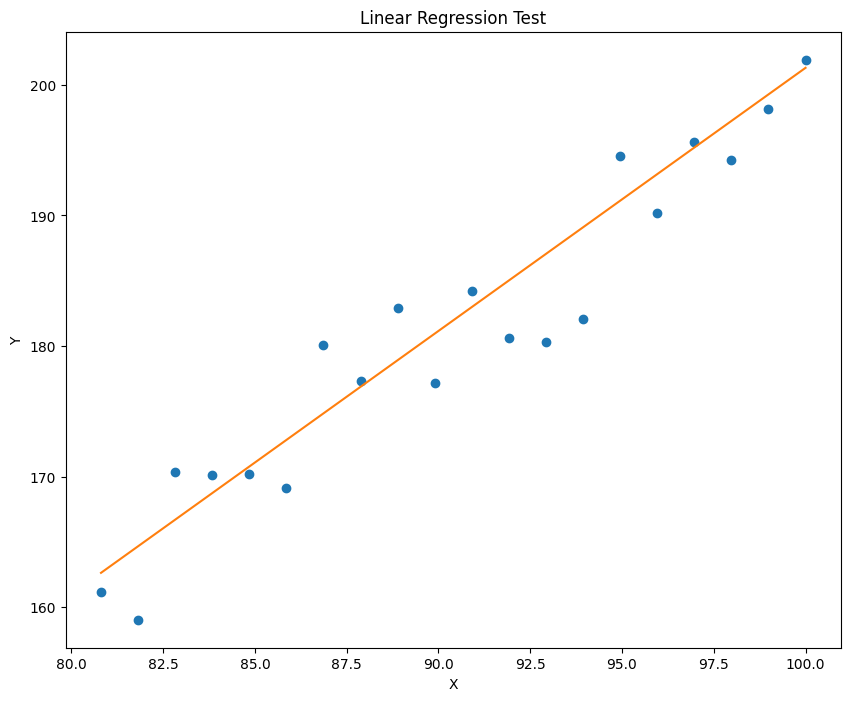
已知模型 y=ax+b,输入浮点数 a,b 并生成加噪后的数据,再利用梯度下降算法迭代得到 a,b。利用的到模型对数据拟合并进行预测,记录误差,并绘制出拟合效果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 import torchimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef generate_noisy_data (a, b, noise_stddev=10 ): a = float (a) b = float (b) x = torch.linspace(0 , 100 , steps=100 , dtype=torch.float32) rand = torch.randn(100 ) * noise_stddev b = b * torch.ones_like(x) y = a * x + b + rand train_x = x[0 :90 ] test_x = x[90 :100 ] train_y = y[0 :90 ] test_y = y[90 :100 ] return train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y def linear_regression (train_x, train_y, num_iterations=10000 , learning_rate=0.0001 ): a = torch.rand(1 , requires_grad=True ) b = torch.rand(1 , requires_grad=True ) for i in range (num_iterations): pred = a.expand_as(train_x) * train_x + b.expand_as(train_x) loss = torch.mean((pred - train_y) ** 2 ) if i % 1000 == 0 : print ("loss:" , loss.data) loss.backward() a.data = a.data - learning_rate * a.grad.data b.data = b.data - learning_rate * b.grad.data a.grad.data.zero_() b.grad.data.zero_() return a, b def plot_fit (train_x, train_y, a, b, title="Linear Regression" ): plt.figure(figsize=(10 , 8 )) plt.plot(train_x.data.numpy(), train_y.data.numpy(), 'o' ) plt.plot(train_x.data.numpy(), (a * train_x + b).data.numpy()) plt.title(title) plt.xlabel('X' ) plt.ylabel('Y' ) plt.show() def main (): (a, b) = (2 , 1 ) num_iterations = 10000 learning_rate = 0.0001 train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = generate_noisy_data(a, b) a_hat, b_hat = linear_regression(train_x, train_y, num_iterations, learning_rate) plot_fit(train_x, train_y, a_hat, b_hat, title="Linear Regression Train" ) plot_fit(test_x, test_y, a_hat, b_hat, title="Linear Regression Test" ) if __name__ == "__main__" : main()
输出:
loss: tensor(3678.7781)
loss: tensor(99.0996)
loss: tensor(99.0956)
loss: tensor(99.0920)
loss: tensor(99.0887)
loss: tensor(99.0858)
loss: tensor(99.0831)
loss: tensor(99.0807)
loss: tensor(99.0786)
loss: tensor(99.0766)
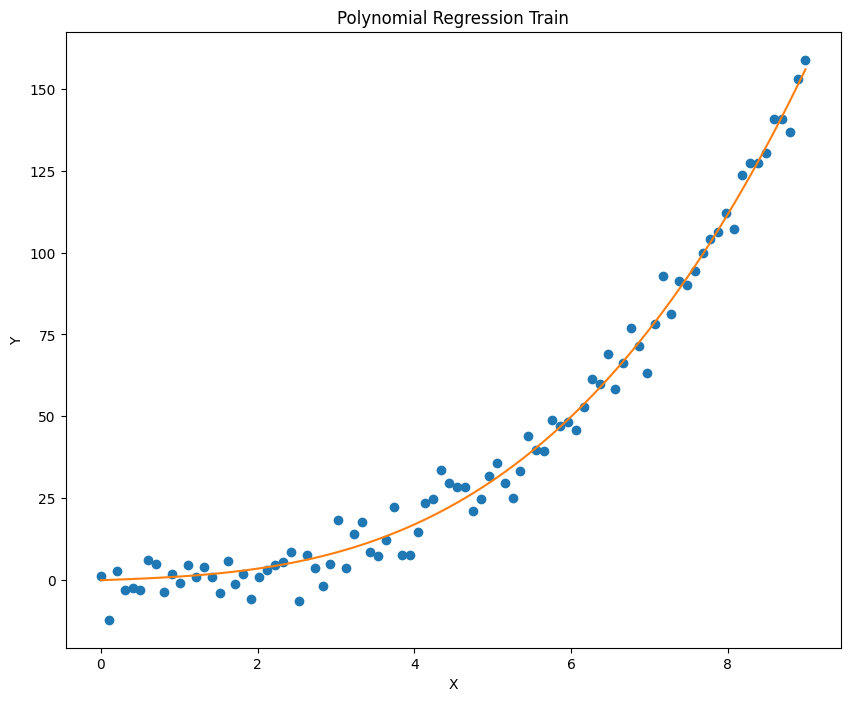
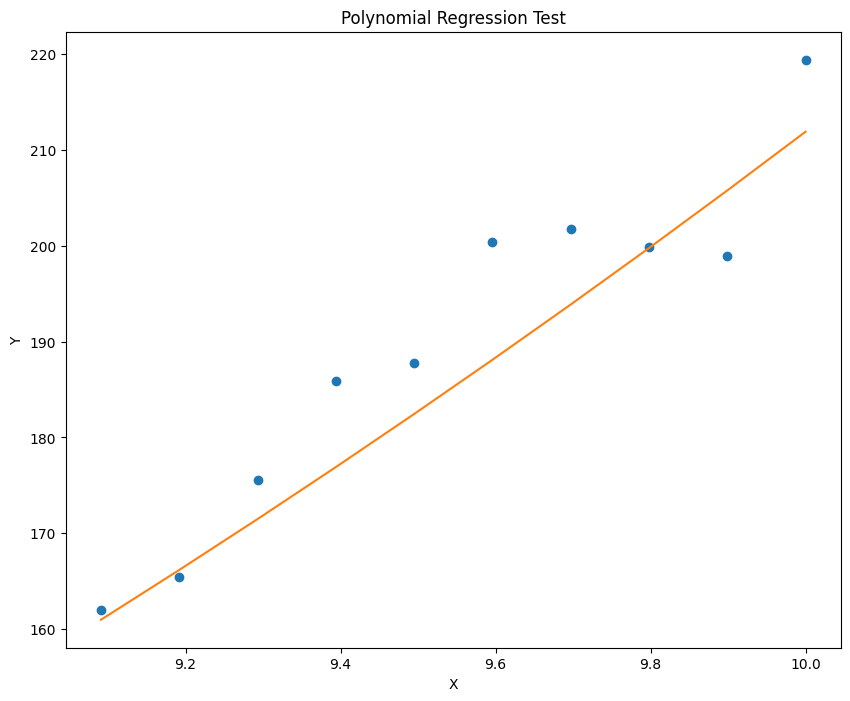
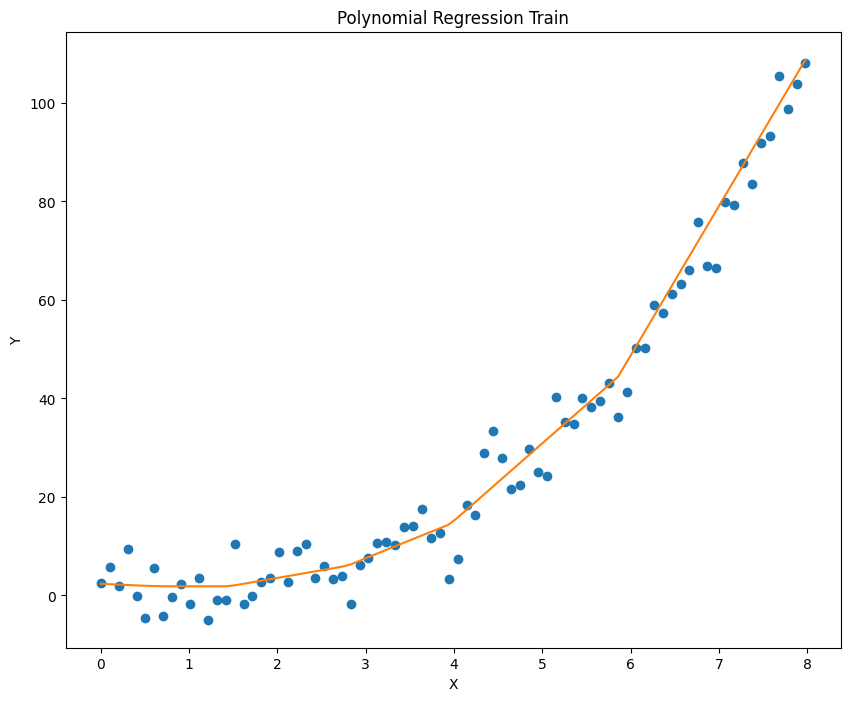
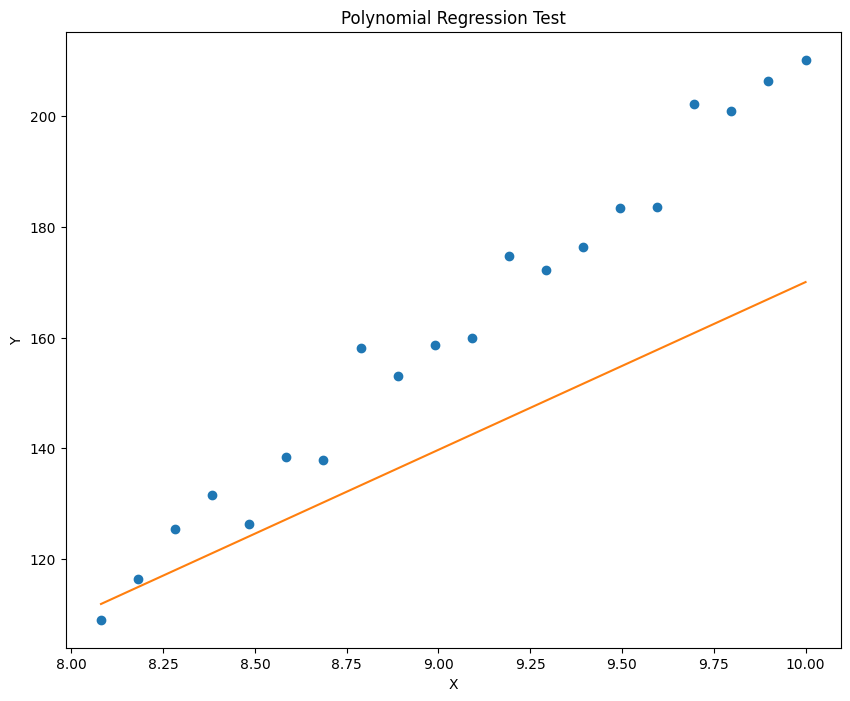
已知模型 y=a*x^3 + b*x^2 + c*x + d,输入浮点数 a,b,c,d 并生成加噪后的数据,再利用梯度下降算法迭代得到 a,b,c,d。利用的到模型对数据拟合并进行预测,记录误差,并绘制出拟合效果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 import torchimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef generate_noisy_data (a, b, c, d, noise_stddev=5 ): a = float (a) b = float (b) c = float (c) d = float (d) x = torch.linspace(0 , 10 , steps=100 , dtype=torch.float32) rand = torch.randn(100 ) * noise_stddev d = d * torch.ones_like(x) y = a * x ** 3 + b * x ** 2 + c * x + d + rand train_x = x[0 :90 ] test_x = x[90 :100 ] train_y = y[0 :90 ] test_y = y[90 :100 ] return train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y def polynomial_regression (train_x, train_y, num_iterations=10000 , learning_rate=0.0001 ): a = torch.rand(1 , requires_grad=True ) b = torch.rand(1 , requires_grad=True ) c = torch.rand(1 , requires_grad=True ) d = torch.rand(1 , requires_grad=True ) for i in range (num_iterations): pred = a.expand_as(train_x) * train_x ** 3 + b.expand_as(train_x) * train_x ** 2 + c.expand_as( train_x) * train_x + d.expand_as(train_x) loss = torch.mean((pred - train_y) ** 2 ) if i % 1000 == 0 : print ("loss:" , loss.data) loss.backward() a.data = a.data - learning_rate * a.grad.data b.data = b.data - learning_rate * b.grad.data c.data = c.data - learning_rate * c.grad.data d.data = d.data - learning_rate * d.grad.data a.grad.data.zero_() b.grad.data.zero_() c.grad.data.zero_() d.grad.data.zero_() return a, b, c, d def plot_fit (train_x, train_y, a, b, c, d, title="Polynomial Regression" ): plt.figure(figsize=(10 , 8 )) plt.plot(train_x.data.numpy(), train_y.data.numpy(), 'o' ) plt.plot(train_x.data.numpy(), (a * train_x ** 3 + b * train_x ** 2 + c * train_x + d).data.numpy()) plt.title(title) plt.xlabel('X' ) plt.ylabel('Y' ) plt.show() def main (): (a, b, c, d) = (0.2 , 0.15 , 0.1 , 0.05 ) num_iterations = 10000 learning_rate = 0.00001 train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = generate_noisy_data(a, b, c, d) a_hat, b_hat, c_hat, d_hat = polynomial_regression(train_x, train_y, num_iterations, learning_rate) plot_fit(train_x, train_y, a_hat, b_hat, c_hat, d_hat, title="Polynomial Regression Train" ) plot_fit(test_x, test_y, a_hat, b_hat, c_hat, d_hat, title="Polynomial Regression Test" ) if __name__ == "__main__" : main()
输出:
loss: tensor(174.3713)
loss: tensor(27.0408)
loss: tensor(26.6397)
loss: tensor(26.5540)
loss: tensor(26.5305)
loss: tensor(26.5192)
loss: tensor(26.5106)
loss: tensor(26.5025)
loss: tensor(26.4947)
loss: tensor(26.4870)
神经网络模型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 import torchimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.nn.functional as Fdef generate_noisy_data (a, b, noise_stddev=5 ): a = float (a) b = float (b) x = torch.linspace(0 , 100 , steps=100 , dtype=torch.float32) rand = torch.randn(100 ) * noise_stddev y = a * x + b + rand train_x = x[0 :80 ] test_x = x[80 :100 ] train_y = y[0 :80 ] test_y = y[80 :100 ] return train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y class Model (nn.Module): def __init__ (self ): super ().__init__() self.out = nn.Linear(1 , 1 ) def forward (self, x ): x = self.out(x) return x def neural_network (net, loss_fn, opt, train_x, train_y, num_iterations=10000 ): for i in range (num_iterations): pred = net(train_x.view(-1 , 1 )) loss = loss_fn(pred, train_y.view(-1 , 1 )) if i % 2000 == 0 : print ("loss:" , loss.data) opt.zero_grad() loss.backward() opt.step() def plot_fit (net, train_x, train_y, title="Polynomial Regression" ): plt.figure(figsize=(10 , 8 )) plt.plot(train_x.data.numpy(), train_y.data.numpy(), 'o' ) plt.plot(train_x.data.numpy(), net(train_x.view(-1 , 1 )).data.numpy()) plt.title(title) plt.xlabel('X' ) plt.ylabel('Y' ) plt.show() def main (): (a, b) = (2 , 1 ) train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = generate_noisy_data(a, b) net = Model() loss_fn = torch.nn.MSELoss(); opt = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.0001 ) num_iterations = 10000 neural_network(net, loss_fn, opt, train_x, train_y, num_iterations) plot_fit(net, train_x, train_y, title="Linear Regression Train" ) plot_fit(net, test_x, test_y, title="Linear Regression Test" ) print (net(test_x.view(-1 , 1 ))) if __name__ == "__main__" : main()
输出:
loss: tensor(4889.4863)
loss: tensor(28.3156)
loss: tensor(28.3152)
loss: tensor(28.3149)
loss: tensor(28.3146)
tensor([[162.6327],
[164.6684],
[166.7040],
[168.7396],
[170.7753],
[172.8109],
[174.8465],
[176.8822],
[178.9178],
[180.9534],
[182.9891],
[185.0247],
[187.0603],
[189.0960],
[191.1316],
[193.1672],
[195.2029],
[197.2385],
[199.2741],
[201.3098]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)
y=a*x^3 + b*x^2 + c*x + d
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 import torchimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.nn.functional as Fdef generate_noisy_data (a, b, c, d, noise_stddev=5 ): a = float (a) b = float (b) c = float (c) d = float (d) x = torch.linspace(0 , 10 , steps=100 , dtype=torch.float32) rand = torch.randn(100 ) * noise_stddev y = a * x ** 3 + b * x ** 2 + c * x + d + rand train_x = x[0 :80 ] test_x = x[80 :100 ] train_y = y[0 :80 ] test_y = y[80 :100 ] return train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y class Model (nn.Module): def __init__ (self ): super ().__init__() self.hidden1 = nn.Linear(1 , 5 ) self.hidden2 = nn.Linear(5 , 10 ) self.hidden3 = nn.Linear(10 , 5 ) self.out = nn.Linear(5 , 1 ) def forward (self, x ): x = self.hidden1(x) x = F.relu(x) x = self.hidden2(x) x = F.relu(x) x = self.hidden3(x) x = F.relu(x) x = self.out(x) return x def neural_network (net, loss_fn, opt, train_x, train_y, num_iterations=10000 ): for i in range (num_iterations): pred = net(train_x.view(-1 , 1 )) loss = loss_fn(pred, train_y.view(-1 , 1 )) if i % 2000 == 0 : print ("loss:" , loss.data) opt.zero_grad() loss.backward() opt.step() def plot_fit (net, train_x, train_y, title="Polynomial Regression" ): plt.figure(figsize=(10 , 8 )) plt.plot(train_x.data.numpy(), train_y.data.numpy(), 'o' ) plt.plot(train_x.data.numpy(), net(train_x.view(-1 , 1 )).data.numpy()) plt.title(title) plt.xlabel('X' ) plt.ylabel('Y' ) plt.show() def main (): (a, b, c, d) = (0.2 , 0.15 , 0.1 , 0.05 ) train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = generate_noisy_data(a, b, c, d) net = Model() loss_fn = torch.nn.MSELoss(); opt = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.0001 ) num_iterations = 10000 neural_network(net, loss_fn, opt, train_x, train_y, num_iterations) plot_fit(net, train_x, train_y, title="Polynomial Regression Train" ) plot_fit(net, test_x, test_y, title="Polynomial Regression Test" ) print (net(test_x.view(-1 , 1 ))) if __name__ == "__main__" : main()
输出:
loss: tensor(1880.3951)
loss: tensor(39.4567)
loss: tensor(33.8119)
loss: tensor(25.3780)
loss: tensor(21.3543)
tensor([[111.8431],
[114.9060],
[117.9690],
[121.0319],
[124.0948],
[127.1578],
[130.2207],
[133.2837],
[136.3466],
[139.4095],
[142.4725],
[145.5354],
[148.5984],
[151.6613],
[154.7242],
[157.7872],
[160.8501],
[163.9130],
[166.9760],
[170.0389]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)